Duodenal Switch
Introduction
Duodenal switch surgery combines the benefits of malabsorptive and restrictive weight loss surgeries and it´s also known as DS or biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. This procedure decreases the quantity of food that can be accommodated by the stomach and also decreases the assimilation of food (the number of calories absorbed and used by the body).
About the procedure
Duodenal switch surgery is a modification of the Biliopancreatic Diversion (BPD) procedure, a type of malabsorptive weight loss surgery. BPD may bring to the patient several associated risks such as ulcers, dumping syndrome, and serious protein-energy malnutrition. Duodenal switch overcomes these problems substantially whilst providing the same positive elements brought by the BPD procedure.
The left half part of the stomach is permanently removed, creating a crescent-like stomach shape
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide weight loss surgeries in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
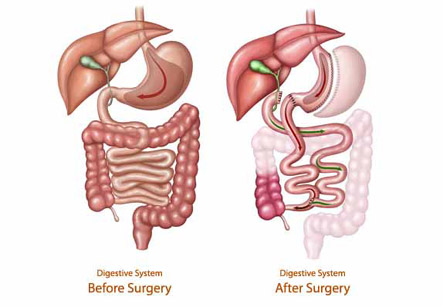
The primary aspect of a duodenal switch operation is perhaps the malabsorptive aspect, this is done by bypassing a large part of the small intestine. The most important steps of this bariatric surgery are listed as follows:
1. The total length of the small intestine is 20 feet or so. It is cut at two locations
2. One cut is made about one to two inches after the pyloric valve of the stomach and then another cut is made eight feet from the lower end of the small intestine. The lower eight foot part is called as the alimentary limb, this is then connected to the first part of duodenum – the first 10 to 12” of small intestine-near the stomach outlet
3. The cut out part of the small intestine is called the biliopancreatic limb. This limb in which most of the process of digestion occurs is totally bypassed, still transporting bile and pancreatic secretions, but reconnected instead near the cut-end of the small intestine
4. The common section where the food and pancreatic digestive enzymes meet is called common limb. Due to the shortness of this section of the intestine involved in digestion, the absorptive area for various nutrients and calories is greatly reduced, thus helping to achieve weight loss
The other part of the surgery causes restrictive weight loss, done as follows:
1. In duodenal switch surgery the left half part of the stomach is permanently removed, creating a crescent like stomach shape which is about the size of a banana, and it decreases the capacity of the stomach and the amount of food eaten. As a result, it produces early satiety even with small quantities of food
2. Less food reduction compared with a gastric bypass surgery or adjustable gastric banding
3. The right side of the stomach is left intact. The benefit of this is that the pylorus, which is the stomach valve that controls the time period between food leaving the stomach and entering the intestines, is not removed. The incidence of dumping syndrome or the syndrome of the quick emptying of food in the small intestine is reduced. This is is an issue perhaps more commonly associated with gastric bypass surgery.
Advantages of the procedure
1. Larger quantities of food can be eaten by the patient compared to other bariatric procedures like Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or adjustable gastric banding. Overall, indications show that there’s a higher degree of patient satisfaction in regards to eating habits working well around DS.
2. This surgery gives more significant and long lasting weight loss due to malabsorption involved
3. No dumping syndrome as the pyloric valve remains intact
4. Reduced risk of stomach ulcers or ulcers of open ends of intestine
5. The intestinal diversion can be reversed if necessary for medical reasons as no part of the small intestine is removed in this surgery
6. The associated conditions with obesity like diabetes mellitus type 2 and high blood pressure also improve after duodenal switch surgery
7. It may be prescribed for patients with an abnormally high BMI (greater than 55).
Considerations
1. There is a period of intestinal adaptation causing frequent bowel movements (4-6 per day).
2. Bloating and frequent passage of foul smelling gases
3. Intolerance for certain foods can develop (it varies by patient).
4. More gallstone problems.
5. Rapid weight loss may cause temporary hair loss in some patients
6. Permanent monitoring for protein malnutrition, anemia and bone disease as well as vitamin supplements.